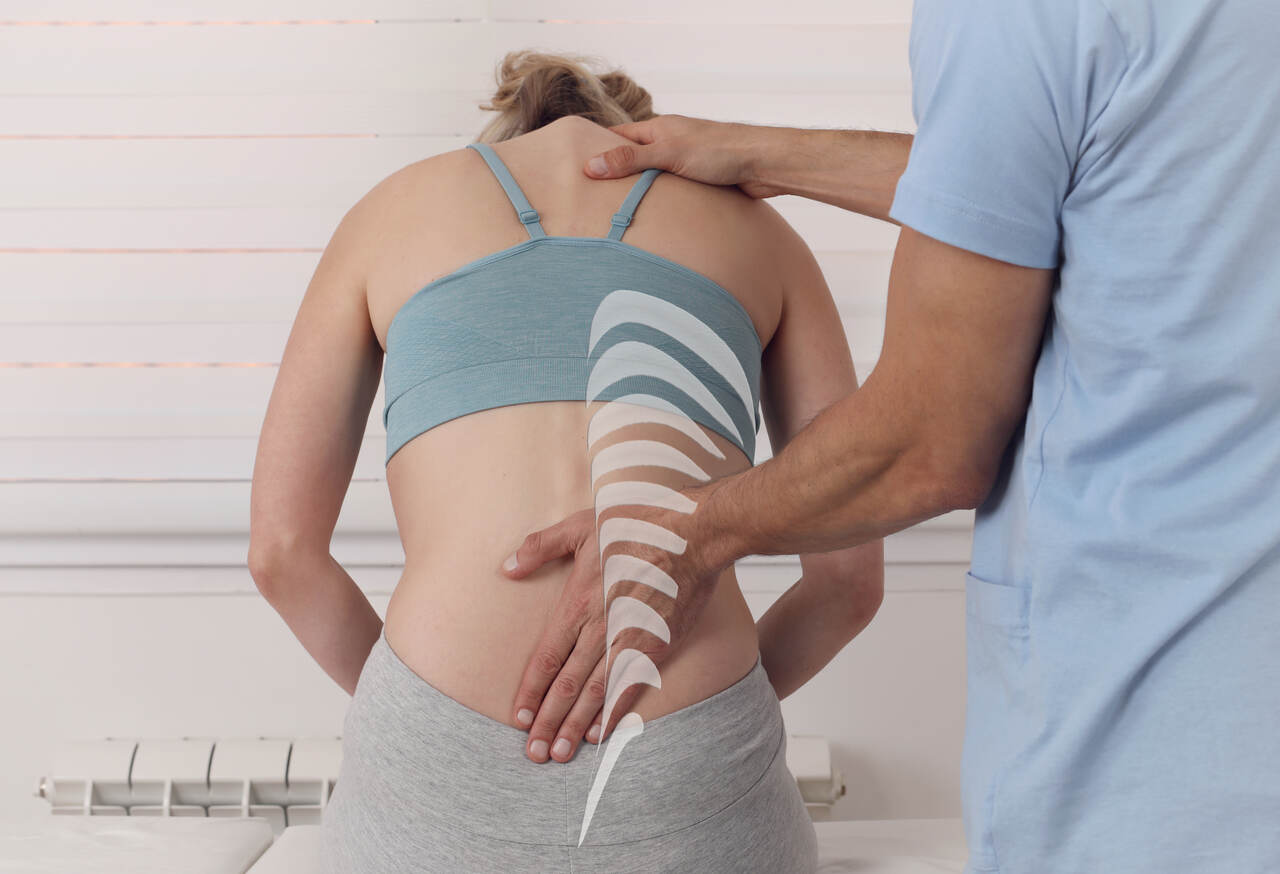
Understanding Posture and its Impact
Importance of Good Posture
Maintaining good posture is essential for your overall health and well-being. Proper posture aligns your body in a way that puts the least strain on supporting muscles and ligaments during movement or weight-bearing activities. Good posture can:
- Reduce back and neck pain
- Improve breathing
- Enhance digestion
- Increase energy levels
- Boost confidence
Proper posture is key in preventing chronic conditions and maintaining a balanced body structure. To learn more about exercises that can help improve your posture, visit our section on posture improvement exercises.
Common Postural Issues
Many individuals suffer from poor posture due to a variety of factors, such as prolonged sitting, incorrect lifting techniques, or even sleeping positions. Common postural issues include:
- Forward Head Posture: The head juts forward, causing neck and shoulder strain.
- Rounded Shoulders: Shoulders hunch forward, leading to upper back pain.
- Anterior Pelvic Tilt: The pelvis tilts forward, causing lower back discomfort.
- Scoliosis: A lateral curvature of the spine that can lead to asymmetry and pain.
| Postural Issue | Description | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Forward Head Posture | Head positioned in front of the body’s center line | Neck and shoulder pain |
| Rounded Shoulders | Shoulders slouch forward | Upper back discomfort |
| Anterior Pelvic Tilt | Pelvis tilts forward, increasing lumbar curve | Lower back ache |
| Scoliosis | Abnormal, lateral curvature of the spine | Back pain, uneven shoulders |
Understanding these common postural issues can help you recognize and address them early. Physiotherapy plays a pivotal role in diagnosing and treating these misalignments through comprehensive assessments and targeted interventions. For detailed insight on how physiotherapy can help with postural realignment, read more about physiotherapy for postural correction.
Role of Physiotherapy in Postural Correction
How Physiotherapy Addresses Postural Problems
Physiotherapy is essential in addressing postural issues by targeting the root causes of misalignment and providing comprehensive solutions. Trained physiotherapists use various techniques to evaluate your posture and design a personalized treatment plan to correct imbalances.
- Assessment and Diagnosis: A detailed physiotherapy assessment identifies specific postural problems. This may involve visual checks, measurements, and mobility tests.
- Stretching and Strengthening: Specific stretching and strengthening exercises are prescribed to target weak or tight muscles, improving flexibility and strength.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques like manual therapy apply pressure to soft tissues and joints to enhance mobility and correct posture.
- Education and Ergonomics: Physiotherapists educate you on maintaining proper posture in daily activities and suggest ergonomic adjustments at work and home.
Benefits of Physiotherapy for Postural Correction
Engaging in physiotherapy for postural correction offers several advantages that extend beyond mere aesthetics. Here are some key benefits:
- Pain Relief: Correcting posture can alleviate chronic pain, particularly in the neck, back, and shoulders. This is often achieved through pain management physiotherapy.
- Improved Mobility: Enhanced flexibility and strength facilitate better movement and reduce the risk of injuries. This is crucial for sports injury rehabilitation.
- Enhanced Performance: Better posture leads to improved physical performance, whether in sports or everyday activities. Techniques are tailored within a personalized physiotherapy plan.
- Reduced Future Injuries: Proper alignment decreases the likelihood of injuries. Incorporating injury prevention programs as part of the treatment helps maintain long-term health.
| Physiotherapy Benefits | Impact on Posture |
|---|---|
| Pain Relief | Reduces chronic pain in targeted areas |
| Improved Mobility | Increases range of motion and flexibility |
| Enhanced Performance | Boosts physical abilities and efficiency |
| Reduced Future Injuries | Minimizes the risk of repetitive strain |
By addressing and rectifying postural misalignments through physiotherapy, you can significantly improve your overall well-being. Explore more on personalizing your treatment plan in our article on personalized physiotherapy plan.
Assessing Your Posture
Before starting physiotherapy for postural correction, it’s crucial to assess your posture accurately. A proper assessment helps in identifying areas that need attention and forms the foundation for an effective treatment plan.
Postural Assessment Techniques
Physiotherapists use various techniques to evaluate your posture. These techniques help in understanding the alignment of different body parts and in identifying any deviations. Below are some common postural assessment techniques:
- Visual Inspection: The therapist observes your standing and sitting posture from different angles. They look for any asymmetries or misalignments in the shoulders, hips, and spine.
- Palpation: This involves the therapist using their hands to feel the alignment and positioning of your bones and muscles. It helps in detecting muscle tightness or imbalances.
- Plumb Line Test: A plumb line is used to see how your body parts align vertically. You stand next to the line, and the therapist checks if your body parts (head, shoulders, hips, knees, and ankles) are aligned with it.
- Range of Motion (ROM) Tests: These tests measure the flexibility and movement range of different joints and muscles. Limited ROM can indicate postural issues.
For further details on how these assessments are conducted, you can visit our section on physiotherapy assessment.
Identifying Postural Misalignments
Identifying postural misalignments is a critical step in developing an effective treatment plan. Misalignments may arise due to various reasons, such as muscle imbalances, improper ergonomics, or previous injuries. Here are some common postural misalignments and how they are identified:
- Forward Head Posture (FHP): This occurs when your head is positioned forward of your shoulders. It is identified by observing the alignment of your ear with your shoulder.
- Rounded Shoulders: This is when your shoulders are hunched forward. It is noticed during visual inspection and palpation.
- Anterior Pelvic Tilt: This happens when the pelvis tilts forward, causing an exaggerated curve in the lower back. It is identified through the plumb line test and palpation.
- Scoliosis: A lateral curvature of the spine, identified through visual inspection and palpation.
Below is a table summarizing common postural misalignments and their identifying features:
| Postural Misalignment | Identifying Feature |
|---|---|
| Forward Head Posture (FHP) | Head positioned forward of shoulders |
| Rounded Shoulders | Shoulders hunched forward |
| Anterior Pelvic Tilt | Forward tilt of pelvis, exaggerated lower back curve |
| Scoliosis | Lateral curvature of the spine |
Understanding these misalignments is crucial for tailoring a personalized physiotherapy plan that addresses your specific needs. The goal is to correct these misalignments through targeted therapies and exercises, enhancing your overall postural health.
For more tips on maintaining good posture and effective physiotherapy practices, explore our resources on posture improvement exercises and manual therapy options.
Physiotherapy Techniques for Postural Correction
In the realm of physiotherapy for postural correction, several techniques are at your disposal to help you attain and maintain better posture. These techniques are designed to address the specific imbalances and muscle weaknesses that lead to poor posture.
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Physiotherapists often recommend a variety of stretching and strengthening exercises to correct postural issues. These exercises focus on lengthening tight muscles and strengthening weak ones to rebalance your body’s alignment.
Stretching Exercises: Stretching exercises help to elongate muscles that have become shortened due to poor posture. Common areas targeted include the chest, shoulders, and hip flexors.
Strengthening Exercises: Strengthening exercises aim to build up the muscles that are weak and unable to support proper posture. Commonly focused areas include the back, core, and glutes.
Here is a sample table outlining common stretches and the muscles they target:
| Stretch | Target Muscle Group |
|---|---|
| Chest Stretch | Pec Major, Pec Minor |
| Shoulder Stretch | Deltoids, Trapezius |
| Hip Flexor Stretch | Iliopsoas, Rectus Femoris |
For strengthening:
| Strengthening Exercise | Target Muscle Group |
|---|---|
| Rowing Exercise | Rhomboids, Trapezius |
| Plank | Core Muscles |
| Glute Bridges | Gluteus Maximus, Hamstrings |
For a detailed guide on exercises for posture improvement, you can refer to posture improvement exercises.
Manual Therapy for Postural Alignment
Manual therapy involves hands-on techniques that your physiotherapist uses to manipulate your muscles and joints. This practice can help to improve mobility, reduce pain, and enhance posture. Techniques may include muscle energy techniques, soft tissue mobilization, and joint mobilizations.
Manual Therapy Techniques: Your physiotherapist may use mobilization to enhance joint function and alignment. This helps alleviate imbalances causing poor posture.
Soft Tissue Mobilization: This technique involves manipulating the soft tissues, like muscles and fascia, to release tension and improve movement.
Joint Mobilizations: This method improves the mobility and function of your joints, aiding in correcting misalignments.
Learn more about the specific applications of manual techniques in postural correction by visiting our article on manual therapy.
By understanding and utilizing these physiotherapy techniques, you’ll be well on your way to achieving better posture and overall health.
Creating a Postural Correction Plan
Individualized Treatment Plans
When it comes to postural correction, it’s important to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses your specific needs. A personalized approach ensures that each aspect of your posture is evaluated and corrected according to your unique physical attributes and lifestyle. Initially, a comprehensive physiotherapy assessment is conducted to determine the extent of your postural misalignments.
Key components of an individualized treatment plan include:
- Detailed Postural Analysis: Helps in identifying areas of imbalance and weakness.
- Targeted Exercises: Specific stretching and strengthening exercises tailored to your needs.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques like manual therapy to realign your spine and muscles.
- Ergonomic Advice: Guidelines on improving your workplace and home ergonomics.
For more on creating personalized treatment strategies, visit our article on personalized physiotherapy plan.
Consistency and Commitment
Consistency and commitment are crucial for effective postural correction. Regular sessions with your physiotherapist and adherence to prescribed exercises at home can significantly improve your posture over time. Skipping sessions or neglecting exercises can delay progress and result in prolonged discomfort.
To stay committed to your postural correction plan, consider the following tips:
- Set Realistic Goals: Break down your overall goal into manageable milestones.
- Track Your Progress: Keep a journal or use an app to monitor improvements.
- Stay Motivated: Celebrate small victories to stay encouraged.
| Commitment Strategy | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Regular Sessions | Ensures consistent monitoring and adjustments |
| Daily Exercises | Accelerates improvement in posture |
| Progress Tracking | Keeps you motivated and focused |
Creating a successful postural correction plan is a collaborative effort between you and your physiotherapist. By following a personalized treatment plan and staying committed, you can achieve and maintain better posture, reducing the risk of future issues. For additional tips on maintaining posture, visit our article on posture improvement exercises.
Maintaining Postural Health Beyond Physiotherapy
Ensuring that you maintain good posture after physiotherapy is crucial for long-term well-being. Here, we will delve into ergonomic practices and lifestyle adjustments that can help you sustain optimal posture.
Ergonomic Practices
Incorporating ergonomic practices into your daily life can significantly enhance your postural health. These practices are designed to minimize stress on your body by optimizing your work and living environments.
- Workstation Setup: Your computer screen should be at eye level to reduce neck strain. Your chair should support your lower back, and your feet should rest flat on the ground. For more detailed guidance, refer to our article on workplace injury physiotherapy.
- Proper Lifting Techniques: When lifting heavy objects, bend at the knees and keep your back straight. Holding the object close to your body helps distribute the weight more evenly.
- Ergonomic Tools: Utilize ergonomic chairs, keyboards, and mice to support proper alignment.
- Frequent Breaks: Take regular breaks to stretch and move around. This prevents muscles from becoming stiff and helps maintain good posture.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Better Posture
Making certain lifestyle changes can also contribute to better postural health. These adjustments can be integrated into your daily routine to support the benefits gained from physiotherapy.
- Strengthening and Stretching Exercises: Engage in exercises that strengthen your core and back muscles. Incorporate stretches to improve flexibility. For specific exercises, see our guide on posture improvement exercises.
- Consistent Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps maintain muscle tone and posture. Activities like yoga and swimming are excellent for overall body alignment.
- Mindfulness and Body Awareness: Pay attention to your posture throughout the day. Practice mindfulness techniques to become more aware of your body’s alignment.
- Healthy Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on your spine and joints, promoting better posture.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure you have a supportive mattress and pillow. Proper sleep posture can prevent misalignment and discomfort.
- Nutrition and Hydration: A balanced diet and staying hydrated support muscle function and overall health, which are essential for maintaining good posture.
By incorporating these ergonomic practices and lifestyle adjustments, you can ensure that the benefits of physiotherapy for postural correction are sustained. For a comprehensive approach to your rehabilitation and well-being, consider a personalized physiotherapy plan.
Below is a summary table to help you maintain postural health:
| Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Workstation Setup | Monitor at eye level, supportive chair, feet flat on the ground |
| Proper Lifting Techniques | Bend at knees, keep back straight, hold objects close |
| Ergonomic Tools | Use ergonomic chairs, keyboards, mice |
| Frequent Breaks | Regular breaks to stretch and move |
| Strengthening Exercises | Core and back strengthening, flexibility stretches |
| Physical Activity | Regular exercise like yoga and swimming |
| Body Awareness | Mindfulness techniques for posture monitoring |
| Weight Management | Maintain healthy weight to reduce stress on spine |
| Sleep | Supportive mattress and pillow |
| Nutrition | Balanced diet and hydration for muscle function |
Implementing these strategies can greatly contribute to maintaining your postural health beyond the physiotherapy sessions. For more insights on various physiotherapy techniques, check out therapeutic exercise programs and injury prevention programs.

