Vestibular Physiotherapy Victoria & Saanich
Feeling dizzy, unsteady, or off-balance? These symptoms can significantly impact your daily life. At Synergy Health Centre, we specialize in vestibular rehabilitation, providing targeted treatments to help you regain your balance.

Customized Care Plans
Effective Pain Relief
Improved Movements
Don’t Let Pain and Limited Movement Hold You Back
It’s time to take back control of your life and free yourself from the limitations of injury, chronic pain, or post-surgery recovery.
Hear From Our Satisfied Clients
See why our patients trust us to help them achieve their goals.
Discover a Better Life with Synergy Health Centre
Reduced pain
Our team will work with you to create a personalized plan of care to help you manage your pain and achieve your goals.
A sense of empowerment
With a customized plan and expert guidance, you’ll feel in control of your health and well-being.
A team you can rely on
Our friendly and knowledgeable clinicians are always here to answer your questions and help you achieve your goals.
Improved performance in recreation or sport
Whether you’re a weekend warrior or simply enjoy staying active, we can help you perform better and avoid injury.
Improved mobility and function
With a focus on movement and activity, we’ll help you regain your mobility and improve your overall function.
A plan for the future
Our aftercare program will help you maintain your progress and keep you on track for a better future.
What is Vestibular Rehabilitation?
Vestibular rehabilitation is a specialized form of physiotherapy designed to alleviate problems caused by vestibular disorders. These disorders affect the inner ear and brain, leading to dizziness, vertigo, imbalance, and other symptoms. Through a series of customized exercises and therapeutic techniques, vestibular rehabilitation aims to retrain your brain and body to process signals from the vestibular system (eyes, ears, & brain) more effectively, restoring your sense of balance and reducing dizziness.
Our Approach
At Synergy Health Centre, we adopt a holistic and personalized approach to vestibular rehabilitation. Our process begins with a comprehensive assessment to understand your specific symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle. This allows us to create a tailored treatment plan that addresses the root causes of your vestibular issues.
Initial Assessment
During your initial visit, our experienced physiotherapists will conduct a thorough evaluation, which may include:
- Detailed medical history review
- Balance and gait assessment
- Eye movement tests
- Positional tests
This assessment helps us identify the precise nature of your vestibular disorder and formulate an effective treatment plan.
Customized Treatment Plan
Based on the assessment results, we design a personalized rehabilitation program that may include:
- Vestibular Habituation Exercises: These exercises help reduce dizziness by gradually exposing you to movements that trigger symptoms.
- Gaze Stabilization Exercises: These exercises improve your ability to focus on a stationary object during head movement, enhancing visual stability.
- Balance Retraining Exercises: These exercises aim to improve your ability to maintain balance and reduce your risk of falls.
- Manual Therapy: Hands-on techniques to address musculoskeletal issues contributing to your symptoms.
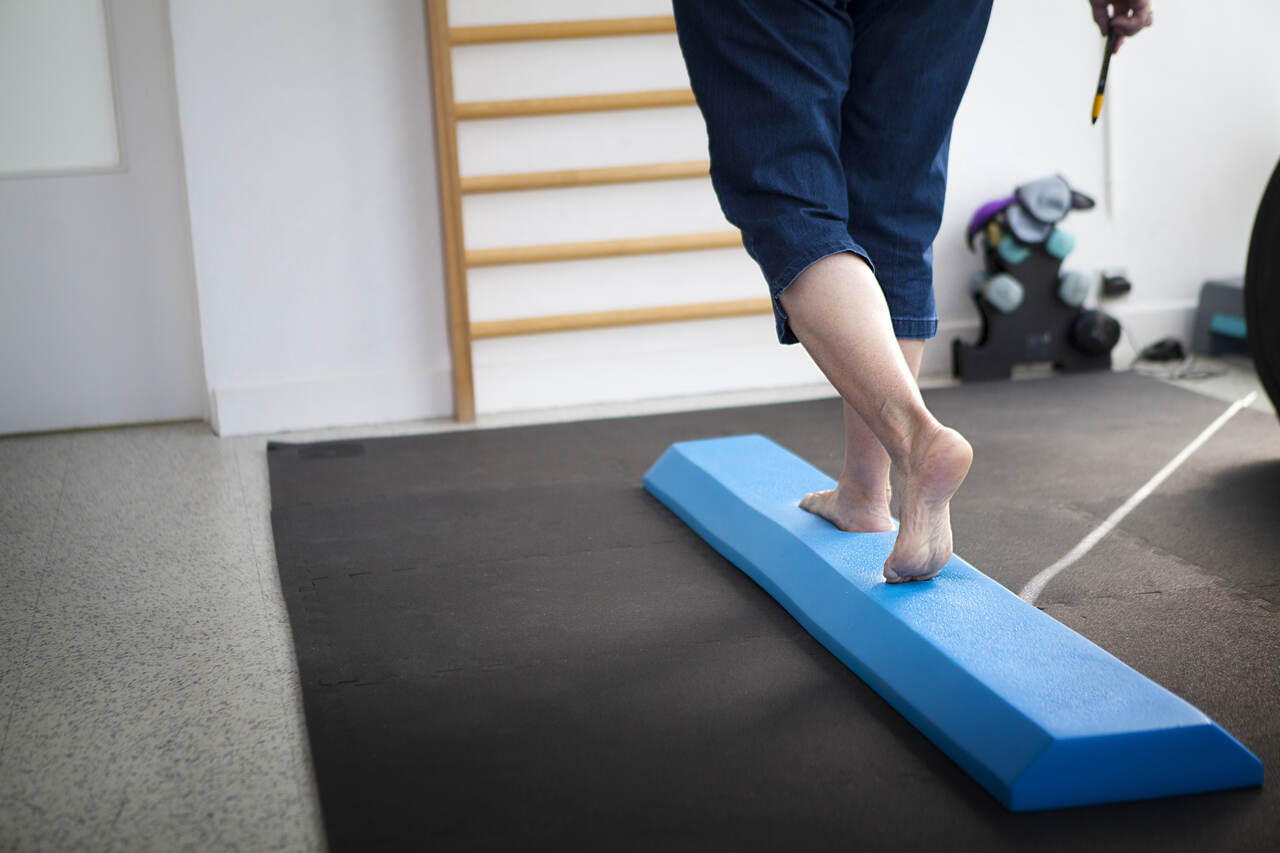

Benefits of Vestibular Rehabilitation
Opting for vestibular rehabilitation offers numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced Dizziness and Vertigo: Targeted vestibular exercises help minimize the frequency and severity of dizziness and vertigo episodes.
- Improved Balance & Reduce Falls: Regain your stability and confidence in daily activities.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Enjoy a more active and fulfilling lifestyle without the constant fear of imbalance.
- Personalized Care: Our individualized approach ensures you receive the most effective treatment for your specific condition.
- Expert Guidance: Our skilled therapists provide continuous support and adjustments to your treatment plan as needed.
Why Choose Synergy Health Centre for Vestibular Rehabilitation?
Synergy Health Centre stands out as a premier provider of vestibular rehabilitation in Victoria. Here’s why you should choose us:
- Experienced Team: Our therapists have extensive training and experience in treating vestibular disorders.
- Comprehensive Care: We offer a holistic approach that addresses both the symptoms and underlying causes of your condition.
- State-of-the-Art Facility: Our clinic is equipped with the latest technology and tools to support your rehabilitation journey.
- Client-Centered Approach: We prioritize your comfort, preferences, and goals throughout the treatment process.
- Proven Results: Our clients consistently report significant improvements in their symptoms and quality of life.
Take the First Step Towards Balance and Wellness
Don’t let vestibular disorders hold you back. At Synergy Health Centre, we are dedicated to helping you overcome dizziness, vertigo, and imbalance through tailored vestibular rehabilitation physio. Our personalized treatment plans are designed to meet your unique needs and restore your quality of life.
Ready to regain your balance and improve your well-being? Contact us today to schedule your initial assessment. Our friendly team is here to answer any questions and guide you on the path to recovery.
Eliminate Pain and Improve Overall Health & Wellness
Our Dedicated Team Provides You with the Best Care
Conditions Vestibular Physiotherapy Can Help You Overcome
Treatments tailored to your unique needs.
|
|
Get on the Path to Pain-Free Living
Book Online or Call Us Today
Booking an appointment is easy and convenient. Simply visit our booking page and select a time slot that works for you or give us a call on (250) 727-3737 to schedule an appointment over the phone. Our friendly staff will be more than happy to help you.
Receive a Custom Care Program
We’ll take the time to understand your unique situation and develop a custom program tailored to your needs and goals. Our team of experienced therapists will work with you to help you achieve your goals.
Accomplish Your Health Goals and Live Pain-Free!
Your custom program is designed to help you achieve your desired outcomes as quickly and effectively as possible. Whether you’re looking to manage your pain, improve your performance in recreation or sport, or simply live a more active and fulfilling life, our team is here to support you every step of the way.
Insurance Partners
We direct bill to most major insurance companies. Check with our staff if your insurance company is included on the list.
Areas We Serve
Vestibular Physiotherapy Victoria & Saanich FAQs
Contact us if you can’t find what you’re looking for.
Synergy Health Centre
Open Hours
Monday – Friday: 7AM – 8PM
Saturday: 8AM – 4PM
Sunday: Closed